
Triacylglycerol: storage forms of fats in the body.Lack hydrogen bonding, so boiling points are lower than related carboxylic acids.

Lactones: Cyclic esters and named similarly to lactones, but with name of precursor acid molecule included.Fischer Esterification: mixing carboxylic acids and alcohols under acidic conditions so that they condense into esters.Named by placing the esterifying group as a prefix and the –oate suffix replaces -oic acid.Esterification Group: substituent that is bonded to the oxygen.Dehydration synthesis products of other carboxylic acid derivatives and alcohols.May or may not participate in hydrogen bonding.Lactams: Cyclic amides and are named according to the carbon atom that is bonded to the nitrogen.Only primary and secondary amines will undergo this reaction.Loss of hydrogen is required for this reaction to take place.
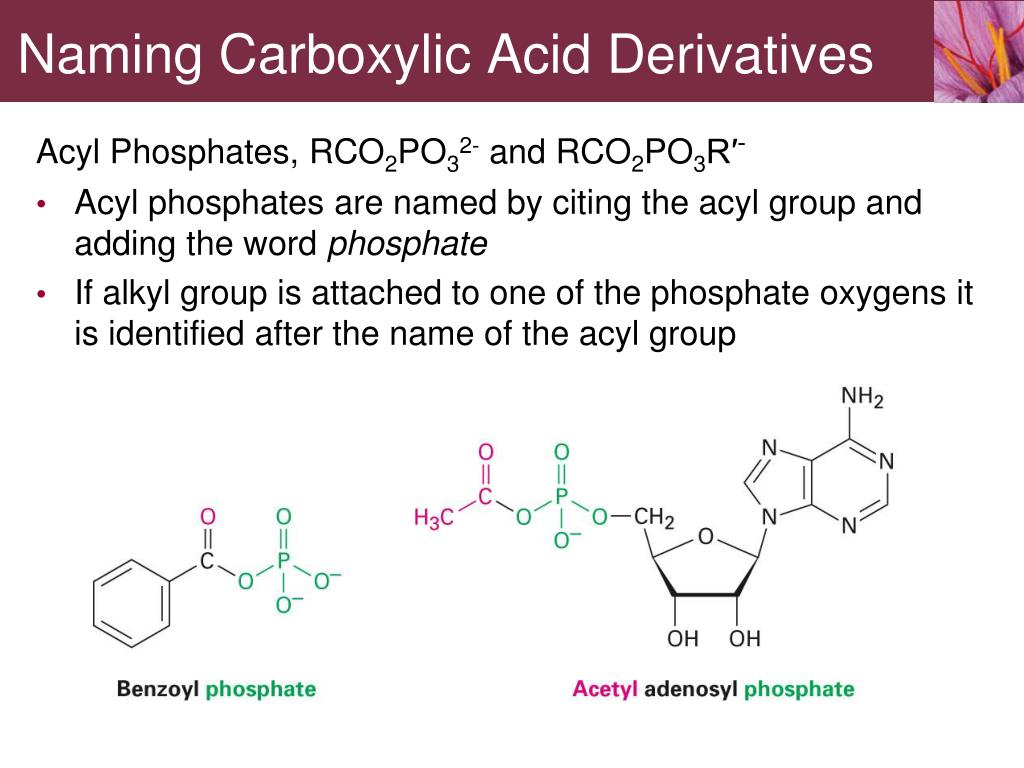
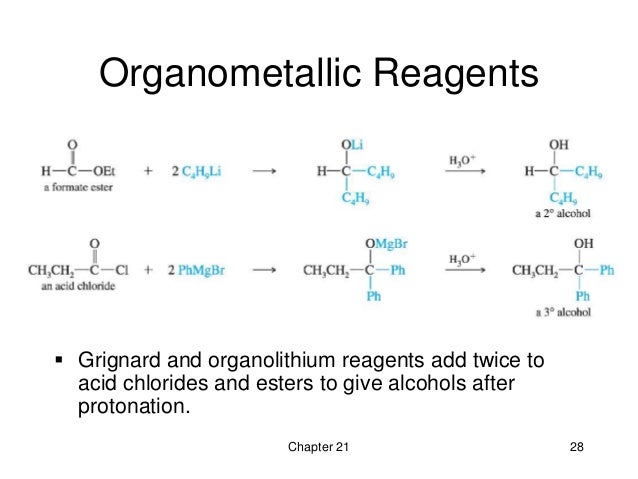
Synthesized by reaction of other carboxylic acid derivatives with either ammonia or an amine.Alkyl substituents on the nitrogen atom are listed as prefixes and their location is specified by the letter N.Named by replacing –oic acid with –amide.These derivatives are formed by a condensation reaction with carboxylic acid in which two molecules combine into one while a small molecule is lost (water in this case).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
